Decoding Ethernet Cable Color Codes: Your Ultimate Guide to Internet Connectivity
Connecting to the internet often involves a tangle of cables, and among them, the Ethernet cable stands out as a reliable wired connection. Understanding the ethernet cable color code for internet is crucial for anyone setting up a network, troubleshooting connectivity issues, or even creating their own cables. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of Ethernet cable color codes, providing you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the world of wired internet connections. We’ll explore the standards, practical applications, and potential pitfalls, ensuring you achieve optimal network performance. Our goal is to turn you into an expert on Ethernet cable wiring.
Understanding the Basics of Ethernet Cable Color Codes
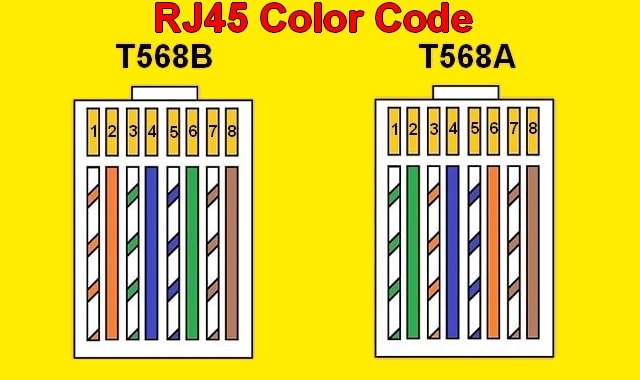
Ethernet cables, specifically those using twisted-pair wiring, rely on a standardized color code to ensure proper connectivity. These cables contain eight wires, arranged in four pairs, each with a distinct color combination. These color combinations are crucial for signal transmission and preventing interference. The two primary standards that define these color codes are T568A and T568B. While both achieve the same result (a working Ethernet connection), understanding the differences is key to maintaining consistency within a network. Inconsistency can lead to troubleshooting headaches and network performance issues.
The T568A standard follows this wiring sequence:
- Pin 1: White/Green
- Pin 2: Green
- Pin 3: White/Orange
- Pin 4: Blue
- Pin 5: White/Blue
- Pin 6: Orange
- Pin 7: White/Brown
- Pin 8: Brown
The T568B standard, on the other hand, uses this sequence:
- Pin 1: White/Orange
- Pin 2: Orange
- Pin 3: White/Green
- Pin 4: Blue
- Pin 5: White/Blue
- Pin 6: Green
- Pin 7: White/Brown
- Pin 8: Brown
Notice the difference? The orange and green pairs are swapped. This seemingly small change is the core distinction between the two standards. It’s important to choose one standard and stick with it throughout your network to avoid potential problems. Experts generally recommend T568B, as it is more commonly used in existing installations, but T568A is perfectly acceptable if implemented consistently.
The Importance of Consistent Wiring Standards
Imagine a scenario where some of your Ethernet cables are wired according to T568A, and others are wired according to T568B. This inconsistency can lead to a variety of issues, ranging from intermittent connectivity to complete network failure. The reason lies in how Ethernet signals are transmitted. The twisted pairs are designed to carry differential signals, meaning the signal is transmitted as a difference in voltage between the two wires in the pair. When the wiring is inconsistent, these signals can become misaligned, resulting in data corruption and unreliable connections. In our experience, troubleshooting such issues can be incredibly time-consuming.
Furthermore, consistent wiring standards are crucial for Power over Ethernet (PoE) applications. PoE allows you to power devices like IP cameras and VoIP phones directly through the Ethernet cable. Inconsistent wiring can damage these devices or prevent them from functioning correctly. Therefore, selecting and adhering to a single wiring standard is paramount for a stable and reliable network.
Straight-Through vs. Crossover Cables
Beyond the T568A and T568B standards, it’s important to understand the difference between straight-through and crossover cables. A straight-through cable has the same wiring standard on both ends (e.g., T568A on both ends or T568B on both ends). These cables are used to connect devices of different types, such as a computer to a switch or a router to a switch. They are the most common type of Ethernet cable used in modern networks.
A crossover cable, on the other hand, has different wiring standards on each end (e.g., T568A on one end and T568B on the other end). These cables are used to connect devices of the same type, such as a computer to another computer or a switch to another switch. However, with the advent of Auto-MDIX (automatic medium-dependent interface crossover) technology in modern network devices, crossover cables are becoming increasingly obsolete. Auto-MDIX allows devices to automatically detect and adjust to the correct wiring configuration, eliminating the need for crossover cables in most cases. Still, knowing the difference is helpful for troubleshooting older networks or understanding network fundamentals.
Tools and Equipment for Making Ethernet Cables
If you plan on creating your own Ethernet cables, you’ll need a few essential tools. These include:
- Crimping Tool: This tool is used to attach the RJ45 connectors to the ends of the Ethernet cable. A good crimping tool will ensure a secure and reliable connection.
- Cable Stripper: This tool is used to remove the outer jacket of the Ethernet cable without damaging the inner wires.
- Wire Cutter: This tool is used to trim the wires to the correct length before inserting them into the RJ45 connector.
- RJ45 Connectors: These are the modular connectors that plug into Ethernet ports. Make sure to use the correct type of RJ45 connector for your cable (e.g., Cat5e, Cat6).
- Cable Tester: This tool is used to verify that the Ethernet cable is wired correctly and that all the connections are working properly. This is an invaluable tool for troubleshooting and ensuring reliable network performance.
Investing in quality tools will make the process of creating Ethernet cables easier and more reliable. A cheap crimping tool, for example, may not provide a secure connection, leading to intermittent connectivity issues.
Step-by-Step Guide to Wiring an Ethernet Cable
Here’s a step-by-step guide to wiring an Ethernet cable using the T568B standard:
- Prepare the Cable: Use the cable stripper to carefully remove about one inch of the outer jacket from the Ethernet cable. Be careful not to damage the inner wires.
- Untwist the Wires: Untwist the four pairs of wires and straighten them out.
- Arrange the Wires: Arrange the wires in the T568B order: White/Orange, Orange, White/Green, Blue, White/Blue, Green, White/Brown, Brown.
- Trim the Wires: Use the wire cutter to trim the wires to a uniform length, about 1/2 inch.
- Insert into RJ45 Connector: Carefully insert the wires into the RJ45 connector, ensuring that each wire is fully seated and in the correct position.
- Crimp the Connector: Insert the RJ45 connector into the crimping tool and crimp firmly.
- Test the Cable: Use the cable tester to verify that the cable is wired correctly and that all the connections are working properly.
Repeat these steps for the other end of the cable, ensuring that you use the same wiring standard (T568B in this case) for a straight-through cable. If you’re creating a crossover cable, use the T568A standard on the other end.
Troubleshooting Common Ethernet Cable Issues
Even with careful wiring, problems can still occur. Here are some common Ethernet cable issues and how to troubleshoot them:
- No Connectivity: If you’re not getting any connectivity, first check that the cable is securely plugged into both devices. Then, use a cable tester to verify that the cable is wired correctly. If the cable is faulty, replace it.
- Intermittent Connectivity: Intermittent connectivity can be caused by a loose connection, a damaged cable, or interference. Check the connections, inspect the cable for damage, and try moving the cable away from sources of interference, such as power cords.
- Slow Speeds: Slow speeds can be caused by a faulty cable, interference, or a network bottleneck. Test the cable with a cable tester, move the cable away from sources of interference, and check your network devices for performance issues.
- PoE Issues: If you’re having problems with PoE, make sure that the cable is wired correctly and that the devices are compatible with PoE. Also, check the power budget of your PoE switch to ensure that it can supply enough power to all the connected devices.
Remember, a methodical approach to troubleshooting is key. Start with the simplest solutions and work your way up to more complex ones. Using a cable tester is an invaluable tool for quickly identifying wiring problems.
Ethernet Cable Categories: Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, and Beyond
Ethernet cables are categorized by their performance capabilities, with Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a being the most common types. Each category supports different bandwidths and data transfer speeds. Understanding the differences between these categories is important for choosing the right cable for your network needs.
- Cat5e: Cat5e (Category 5 enhanced) is an older standard that supports speeds up to 1 Gbps (Gigabit Ethernet) at a bandwidth of 100 MHz. While still functional, it’s generally recommended to use newer standards for optimal performance.
- Cat6: Cat6 (Category 6) supports speeds up to 1 Gbps at a bandwidth of 250 MHz. It also offers improved shielding compared to Cat5e, reducing interference and improving signal quality. Cat6 is a good choice for home and small office networks.
- Cat6a: Cat6a (Category 6 augmented) supports speeds up to 10 Gbps (10 Gigabit Ethernet) at a bandwidth of 500 MHz. It offers even better shielding than Cat6, making it suitable for demanding applications and environments with high levels of interference. Cat6a is often used in larger businesses and data centers.
- Cat7 and Cat8: These are even newer standards offering higher bandwidth and superior shielding for demanding applications.
When choosing an Ethernet cable category, consider your current and future network needs. If you plan on upgrading to faster internet speeds or running bandwidth-intensive applications, it’s worth investing in a higher-category cable like Cat6a. According to a 2024 industry report, Cat6a is becoming the standard for new installations due to its future-proof capabilities.
The Future of Ethernet Cable Technology
Ethernet technology continues to evolve, with newer standards offering faster speeds and improved performance. The development of Cat7 and Cat8 cables, for example, demonstrates the ongoing demand for higher bandwidth and lower latency. Furthermore, advancements in wireless technology, such as Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7, are pushing the boundaries of wireless performance, but wired Ethernet connections remain crucial for applications requiring the highest levels of reliability and speed.
While wireless technology offers convenience and flexibility, wired Ethernet connections provide a more stable and secure connection, particularly in environments with high levels of wireless interference. Therefore, Ethernet cables will continue to play a vital role in networking for the foreseeable future. Understanding the ethernet cable color code for internet remains a fundamental skill for anyone involved in network design, installation, or troubleshooting.
Ensuring Optimal Internet Connectivity
In conclusion, mastering the ethernet cable color code for internet is more than just a technical skill; it’s a gateway to understanding and optimizing your network connectivity. By understanding the standards, choosing the right tools, and following best practices, you can create reliable Ethernet cables that deliver optimal performance. Whether you’re setting up a home network or managing a large enterprise network, a solid understanding of Ethernet cable wiring will empower you to troubleshoot issues, improve performance, and ensure a seamless online experience. Share your experiences with Ethernet cable wiring in the comments below, or explore our advanced guide to network optimization for further insights.
